Getting Started with Kubernetes
Supported/Verified Managed Cloud K8s
AWS EKS - AmazonLinux (default) and Ubuntu node VMs
GCP GKE - CoS (default) and Ubuntu node VMs
Azure AKS - Ubuntu running default Kubernetes (v1.18) or later.
Canonical MicroK8s
RancherD
Prerequisites
Cluster should have egress port 443 open to allow Araali to talk to the backend.
Araali UI Login
Open a chrome browser and go to Araali Console
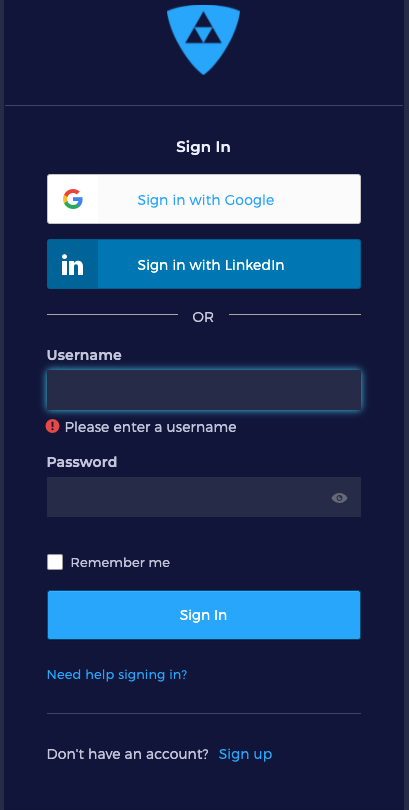
If your email is already registered and your business email uses Google service, then use “Sign in with Google”. Otherwise, click on “Need Help Signing In?” which will open “Forgot Password?”. Then, complete the steps to sign in to the console.
You are in!!
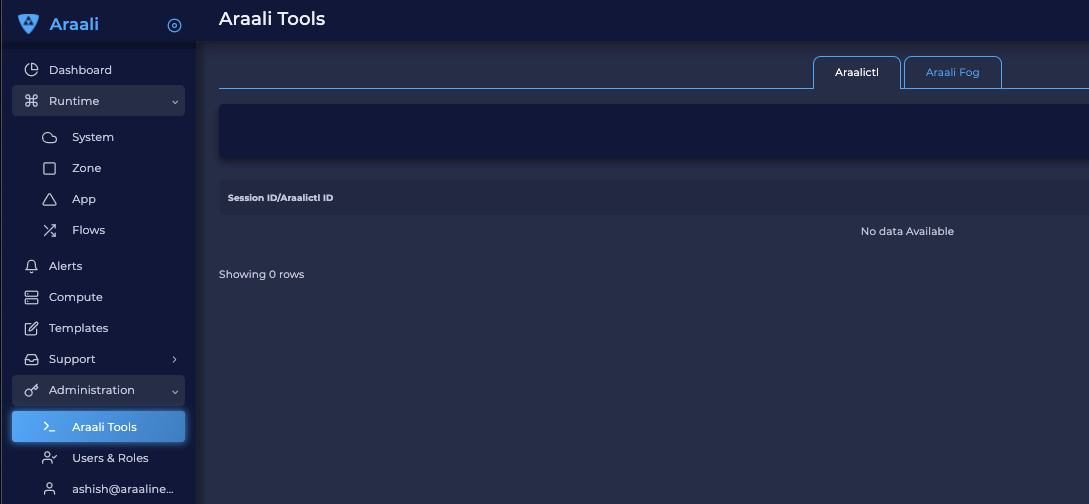
Now, in the left-hand panel, go to Administration and then Araali Tools. You have to come back to this page to authorize Araalictl
Fortifying a k8s Cluster
Follow the steps below to fortify a Kubernetes cluster (same place where your k8s control plane is running).
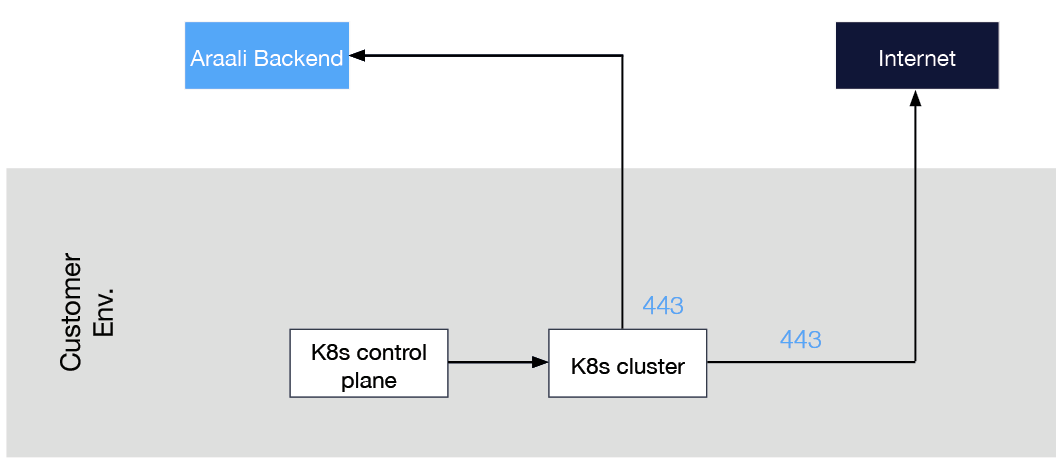
- Download Araalictl
On Linux:
curl -O https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/araalinetworks.cf/araalictl.linux-amd64
On Mac:
curl -O https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/araalinetworks.cf/araalictl.darwin-amd64
Make it executable:
chmod +x araali* ln -sf araali* araalictl
Authorize araalictl:
sudo ./araalictl authorize <email-id>
Now go to Araali UI >> Administration >> Araali Tools to approve the araalictl session.
Check if araalictl is installed:
./araalictl version -v
Check current context, the name with “*” is the one you are pointing to right now:
kubectl config get-contexts
Fortify your cluster, araalictl and kubectl running on the same machine:
./araalictl fortify-k8s -auto -tags=zone=<optional-zone-override> -context=<context of k8s cluster>
Optional: If araalictl and kubectl are not running on the same machine:
# Create yaml file to fortify your cluster
./araalictl fortify-k8s -tags=zone=<optional-zone-override> -context=<context of k8s cluster>
# The above command will generate araali_k8s.yaml file. Copy it to the k8s control plane (where kubectl is running) and then apply
kubectl apply -f araali_k8s.yaml
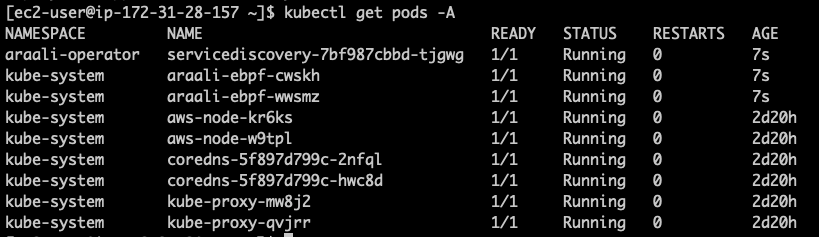
Check if Araali is Installed
Araali should be running in two namespaces (1) araali-operator and (2) kube-system:
kubectl get pods -A
Setting up Araalictl in the CM VM
Download Araalictl
Linux:
curl -O https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/araalinetworks.cf/araalictl.linux-amd64
Mac:
curl -O https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/araalinetworks.cf/araalictl.darwin-amd64
Make it Executable:
chmod +x araali* ln -sf araali* araalictl
Authorize Araalictl:
sudo ./araalictl authorize <email-id>
Check if Araalictl is installed:
./araalictl version -v
Optional - Generate and add ssh-key (if Araalictl is running on the VM you wish to fortify)
If you don’t have id_rsa.pub in your ~/.ssh account:
ssh-keygen
Copy it to authorized_keys to allow ssh localhost:
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
Fortifying target VMs in your Cluster
Fortifying Remotely:
./araalictl fortify-live -fortify -tags=zone=<zone_name>,app=<app_name> vm1
Fortifying Localhost:
./araalictl fortify-live -fortify -tags=zone=<zone_name>,app=<app_name> localhost
Updating Zone, App tags:
./araalictl fortify-live -add -tags=zone=<updated_zone>,app=<updated_app> <remote_user>@<remote_host>
For wider use, we recommend to run Araali on the same machine as your Configuration Management Tool (Ansible, Salt, Puppet, Chef, etc.)
Sample K8s Microservice to Test
Google Cloud Platform eCommerce Demo Clone from Github:
git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/microservices-demo.git
Create namespace or run it in default namespace:
kubectl create ns gshop
Run the microservice:
cd microservices-demo/release kubectl apply -f kubernetes-manifests.yaml -n gshop
get URL of the frontend:
kubectl get svc -A
Araali Dashboard
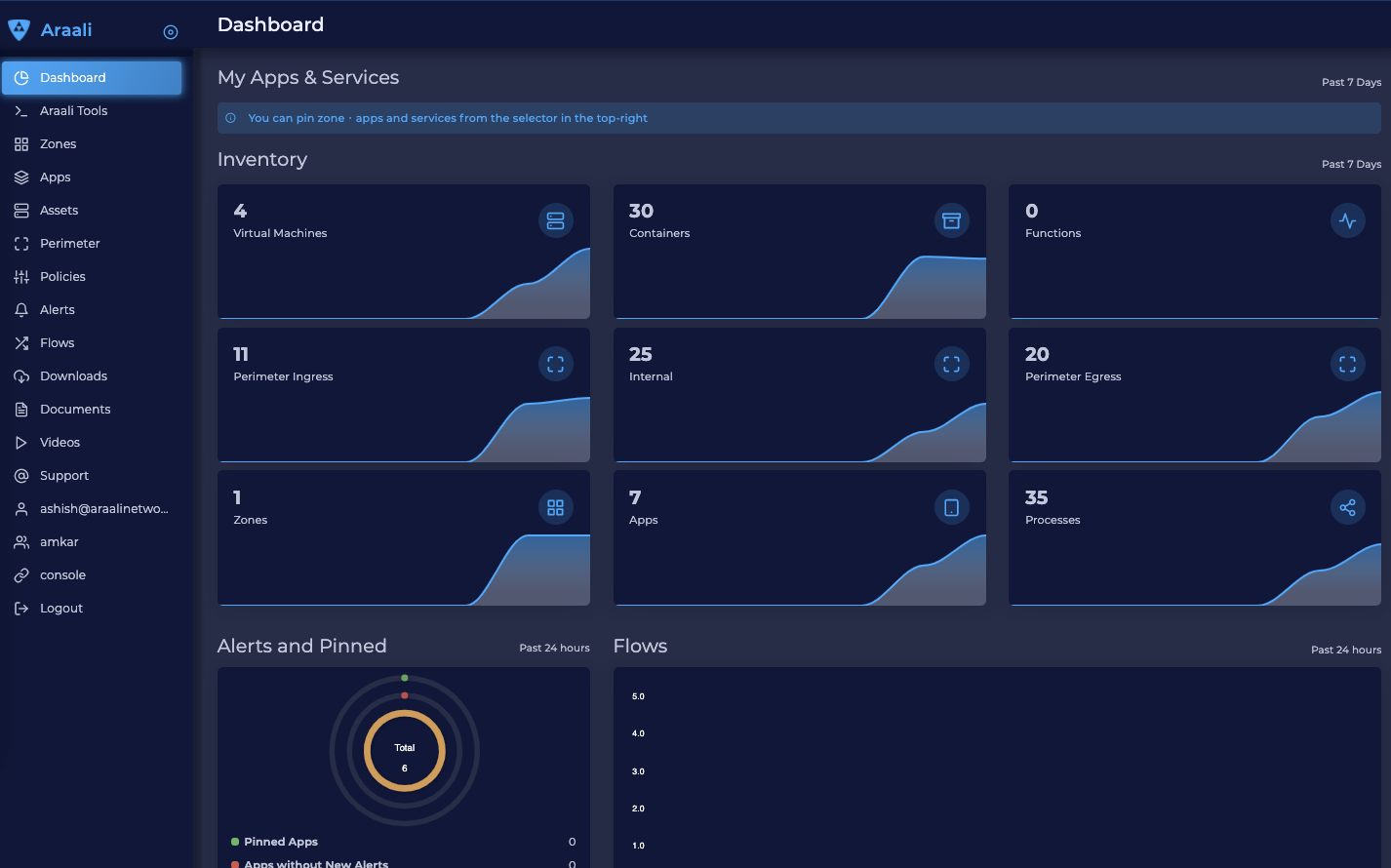
Go back to the Araali UI and click dashboard. You can see an inventory of your assets covered as well as detailed audits of your communication.
To Uninstall Araali
To uninstall if araalictl and kubectl are on the same machine:
./araalictl fortify-k8s -delete -context=<context of k8s cluster>
Otherwise, delete the yaml file:
kubectl delete -f araali_k8s.yaml
To Uninstall Remotely:
./araalictl fortify-live -unfortify <remote_user>@<remote_host>
To Uninstall Locally:
./araalictl fortify-live -unfortify localhost